Have you ever heard of the term megabyte gigabyte, terabyte, or petabyte, but what exactly does it mean when it comes to storage? Let’s take a closer look at storage sizes.
Words like bytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and petabytes all refer to the amount of digital storage. Perhaps some people, confused by terms such as megabit, gigabit or terabyte.
Some of these terms are used when comparing storage media on hard drives (HDDs), and flash storage devices (such as SSDs or flash disks). As well as comparing the speed of internet data transfer if using network services.
Bits, Bytes, dan Kilobytes
First, let’s look at the basics of digital storage with some lower-level capacity bits and bytes so you know the difference.
bit
The smallest unit of storage is called the bit abbreviated as b, using lowercase letters. It is only capable of storing one binary digit—either 1 or 0, nothing else. One megabit is one thousand kilobits, then one kilobit is a thousand bits. If abbreviated megabits are shortened to Mb, kilobits become Kb. So:
- Kilobit (Kb) = 1000 bit.
- Megabit (Mb) = 1000 Kilobit.
- Gigabit (Mb) = 1000 Megabit.
Terms like this are commonly used to measure transfer speeds, for example 20Mbps internet speed and 10 Gb/s USB cables.
Byte
Then one byte (B), with uppercase letters. This is the unit used to declare the data storage capacity.
One Byte is eight bits, and it can store one character of text. So storing a word with 10 characters like “save this” requires 10 Bytes of storage space.
Further from bytes to kilobytes (KB), equivalent to 1,024 bytes of data (or 8,192 bits – multiplied by eight). So the order goes like this:
- 1 Byte = 8 bit (b).
- 1 Kilobyte (KB) = 1024 B.
- 1 Megabyte (MB) = 1024 KB (1.048.576 Byte).
- 1 Gigabyte (MB) = 1024 MB (1.073.741.824 Byte).
- 1 Terabyte (MB) = 1024 GB (1.099.511.627.776 Byte).
- and so on.
Storage media using decimal values
In advertising products all manufacturers use decimal values, such as hard disk products, flash disks or internet quotas, for example; A 1 Terabyte SSD equals 1000 GB instead of 1024. So that led to the question arose, why the storage capacity does not match the original. How to explain it?
This example is the storage capacity of a device of 256 GB. If changed in Decimal bytes the value is multiplied by 1000 three times.
- So 256 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 is 256, 000, 000, 000 Bytes.
- Then we convert it to a binary value (which is used by the computer device system).
- 256.000.000.000 Byte / ( 1024 * 1024 * 1024) =
- The result is 238.41 GB.
The larger your storage capacity, the bigger the difference when read by windows will look bigger.
| Advertised Capacity (Decimal) | Unix/ Mac Reported (Decimal) | Windows Reported (Binary) |
|---|---|---|
| 250 GB | 250 GB | 233 GB |
| 500 GB | 500 GB | 465 GB |
| 1000 GB | 1000 GB | 931 GB |
| 2000 GB | 2000 GB | 1862 GB |
*For Unix/ Mac users the capacity is displayed in decimals, so it complies with the specifications advertised.
*For RAM components the value used is 1024, so will see it running according to the specifications. If you use 16 GB of RAM, then the system will read 16 GB anyway.
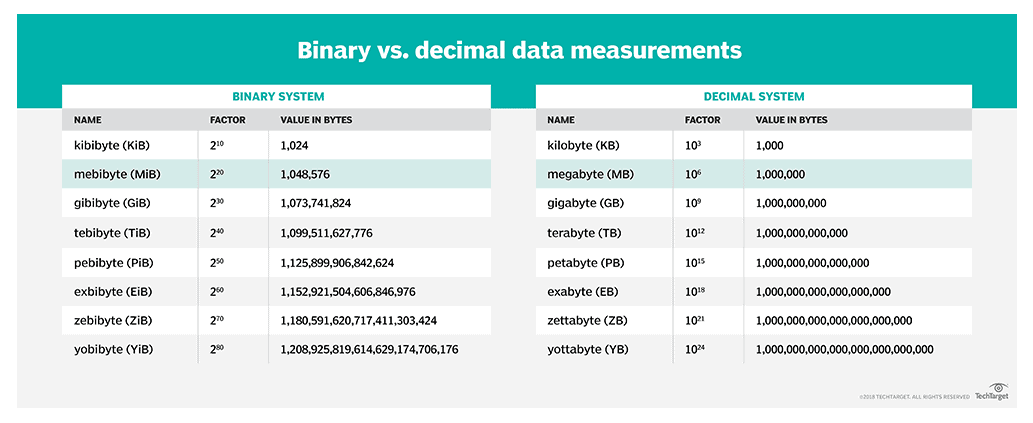
Storage Capacity Order
Here are the tiers of storage capacity names from small to large, some of which we encounter very rarely.
- Bytes (B)
- Kilobytes (KB)
- Megabytes (MB)
- Gigabytes (GB)
- Terabytes (TB)
- Petabytes (PB)
- Exabytes (EB)
- Zettabytes (ZB)
- Yottabytes (YB)
- Brontobytes (BB)
- Geopbyte (GB)
- Saganbyte (SB)
Megabytes (MB)
There are 1,024 KB in one megabyte (MB). Typically, after the kilobyte stage, each subsequent storage is 1,024. Mb data size will definitely be encountered often on our device every day, the size of 5 MB is the average mp3 song (4 minutes).
Gigabyte (GB)
GB is a common thing in storage media. Although most storage is measured in Terabytes, very much hard disk and SSD storage still uses gigabytes of capacity, including flash drives and external hard drives.
7 GB is equivalent to how much data is used per hour to stream Netflix Ultra HD videos.
Terabyte (TB)
1 Terabyte equals to 1,024 GB. In what use is such a large amount of data? For example: about 24 TB of video data uploaded to YouTube per day in 2016.
Petabyte (PB)
There are 1,024 TB (or about one million GB) in one petabyte (PB), greater than TB or GB, starting from here we no longer encounter in everyday life. But for example: about 20 PB of the amount of data processed by Google every day in 2008.
Exabytes (EB)
There are 1,024 PB in one exabytes (EB). Giant companies such as Amazon, Google, and Facebook process an untold amount of data, 15 EB is the total estimated data carried by Google, 1 EB is equal to 11 million 4K videos.
The next capacities for the curious are zettabytes, yottabytes, brontobytes and geopbytes.
Question?
Why is the SSD capacity not true to the original?
Because of SSD manufacturers, it sells it with a rank value of 1000, while computers read with a rank of 1024.
Why does a 500gb hard drive read 465?
For example, a 500gb hard drive is equal to 500,000,000,000 bytes divided by 1024 three times, then the result is 465.6 GB.
How many GB is a 1TB SSD?
1000GB.
The unit used to declare the data storage capacity is.
Byte.
1000 mb how many GB?
1000 mb/1000 = 1 GB.
1 GB how many hours of video?
It is estimated that 1 GB of data can play YouTube 1080p30 for 45 minutes, 720p30 for 1 hour 10 minutes, and 480p30 2 hours 20 minutes.
Internet speed of 10 Mbps fast or not?
Pretty quickly, you can download files around 1.2 MB in 1 second or around 700 MB in 10 minutes. And you can watch Youtube 1080p very smoothly.
